Homeowners
Most homes in the UK are currently heated by fossil fuels. The UK Government has committed to reducing carbon emissions to net zero by 2050 and a key part of achieving this ambition is decarbonising the way we heat our homes.
Heat pumps will play a key part in delivering low carbon heat to homes across the UK. If you are thinking of switching to a heat pump, there are a few things you should know:
A heat pump is an electronic device which draws thermal energy (heat) from an external medium, such as air, or the ground. This is then used to heat the building – via radiators or other emitters, and hot water via a storage cylinder. The heat pump can use your existing radiators; however, your installer may advise you to upgrade these to improve efficiencies and ensure your system is optimised. Heat pumps are highly efficient, operating at 3-4 times the efficiency of a natural gas boiler, whilst producing considerably less emissions. This means that they not only reduce carbon emissions but can also lower energy bills.
To help drive the shift from fossil fuel heating systems to heat pumps, the Government has set an ambition for 600,000 heat pumps installations to be completed per year by 2028. The International Energy Agency predicts that heat pumps will become the main space heating technology worldwide from around 2045. This demonstrates the growing demand for the technology and the important role it will play in our future energy system.
A heat pump will likely cost more to buy and install than a traditional heating system. However, the Government launched the Boiler Upgrade Scheme in April 2022, which offers grants of up to £7,500 to residents in England and Wales replacing a fossil fuel system with a heat pump. Your installer applies for the Boiler Upgrade Scheme grant on your behalf, but they must be Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS) certified. More information about available funding can be found here.
If you live in Scotland, the Home Energy Scotland provides regional advice and financial support. More information about available funding can be found here.
Our members provide a range of heat pump solutions. It is important that you speak to your local installer to find out which system is most appropriate for your home.
There are four commonly installed types of heat pump:
Air source heat pumps
Air Source heat pumps require an external unit. These can either be installed outside of the property or mounted via a window (see illustration right). Heat is extracted from ambient air drawn across its heat exchanger. Air source heat pumps generally tend to be cheaper than other types, due to the comparative ease of installation.
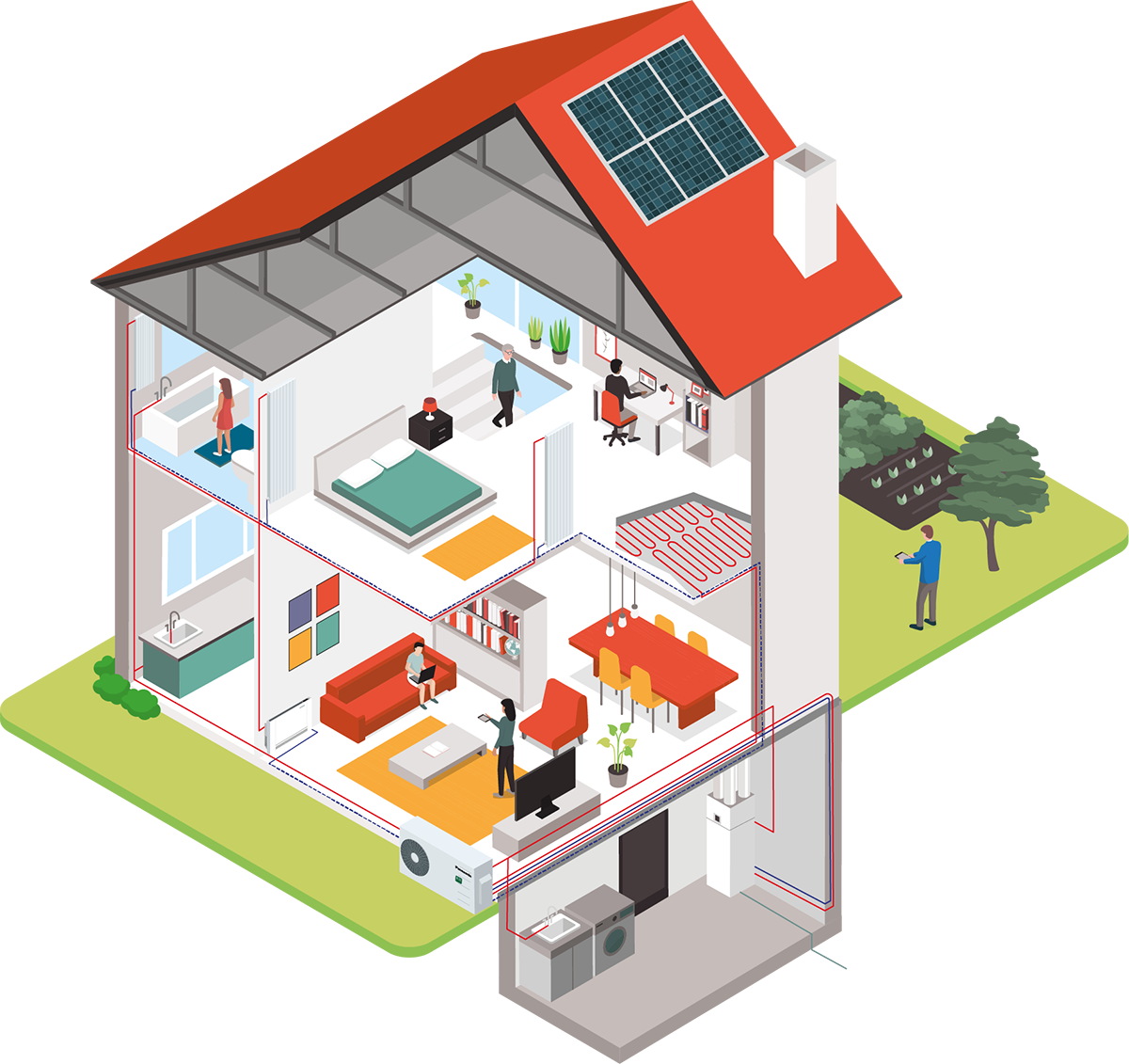

Figure 1 – Illustration of air source heat pump installation in home
Ground source heat pumps
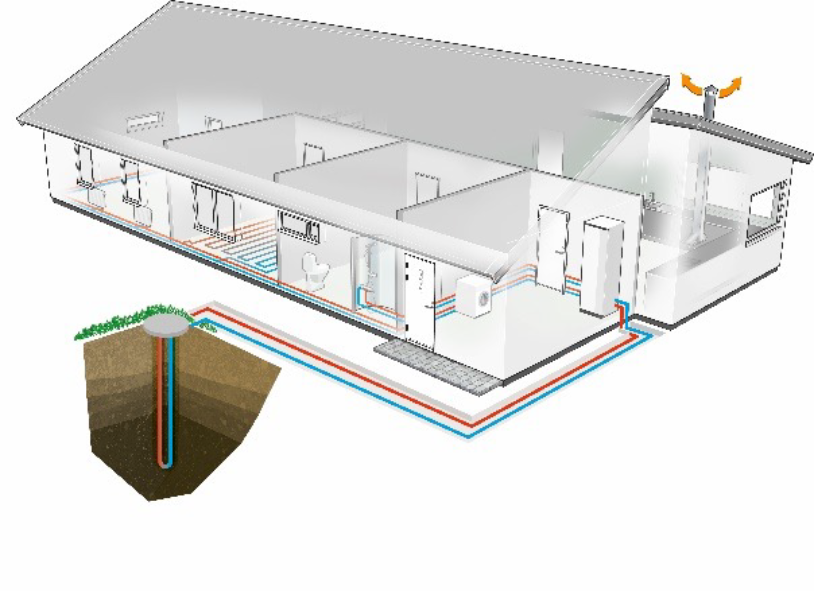
Figure 2 – Illustration of ground source heat pump installation in home with bore hole
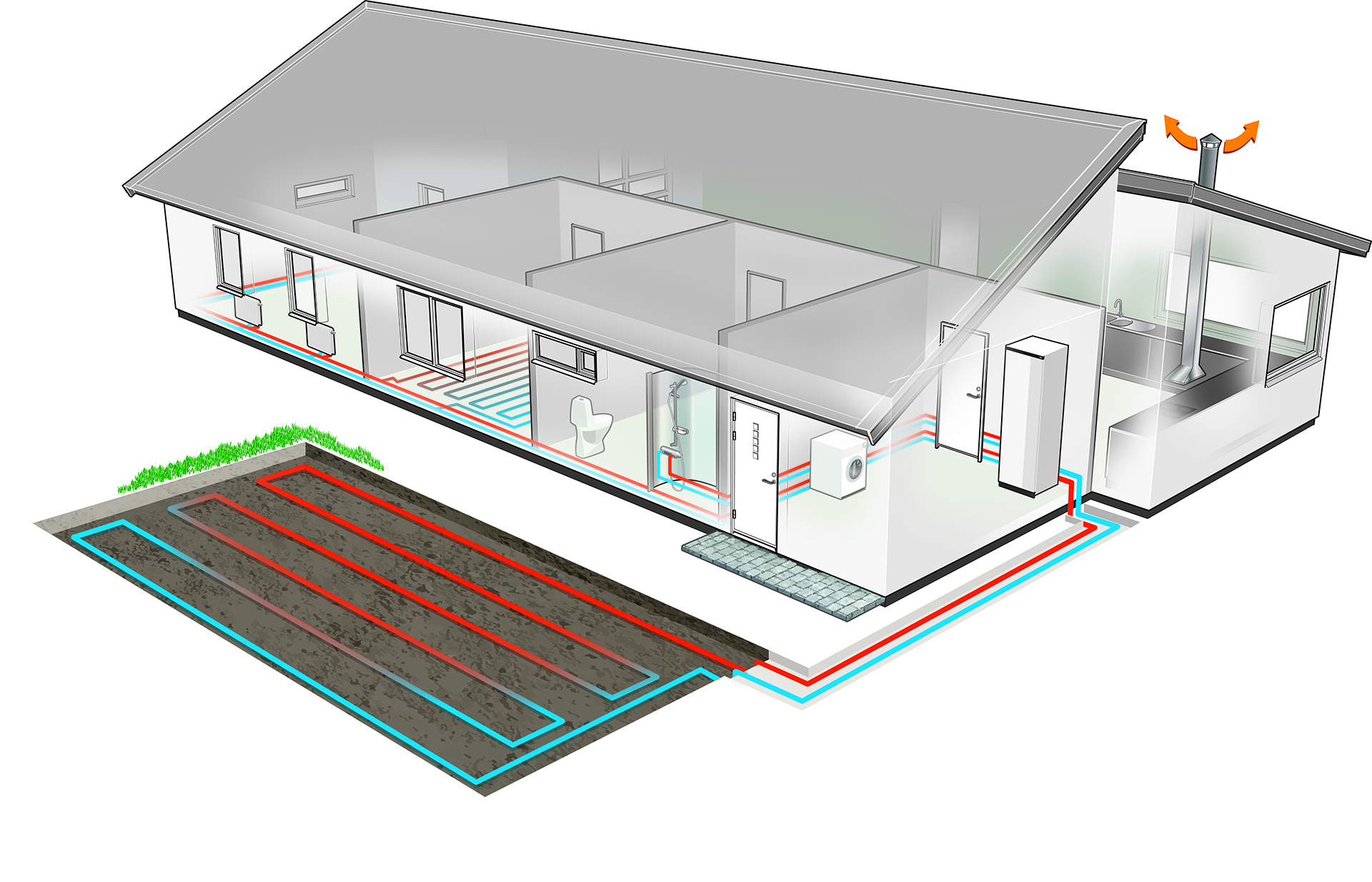
Figure 3 – Illustration of ground source heat pump installation in home with horizonal loop
Ground source heat pumps use thermal energy from the ground. The unit sits indoors but takes thermal energy from the ground. A closed pipe-work loop of water/antifreeze solution is buried in the ground, either vertically via boreholes or horizontally in trenches (coiled or straight lengths), alongside the heat pump used to extract the heat. The groundworks associated with the installation of these systems accounts for why they are often more costly to install than an air source heat pump. However, they are more efficient.
Water source heat pumps
Water Source heat pumps are similar to ground source heat pumps, in that they draw thermal energy from an external medium. There are two types of water source heat pump: closed loop and open loop. These systems use a pump to move water around a loop, drawing heat for the home. Water source heat pumps tend to run extremely efficiently, given that water is such a good conductor of heat.
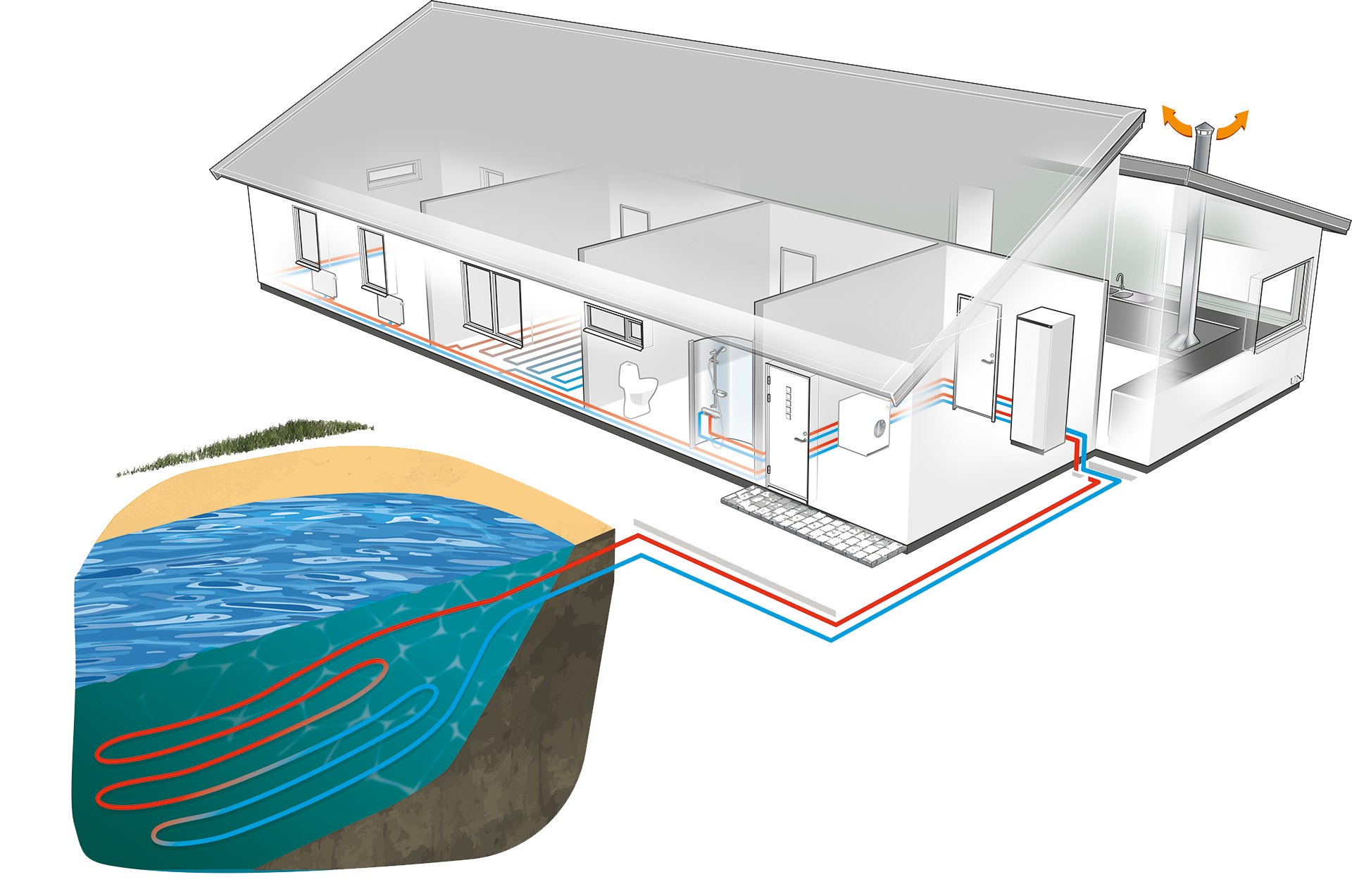
Figure 4 – Illustration of water source heat pump installation in home
Hybrid source heat pumps
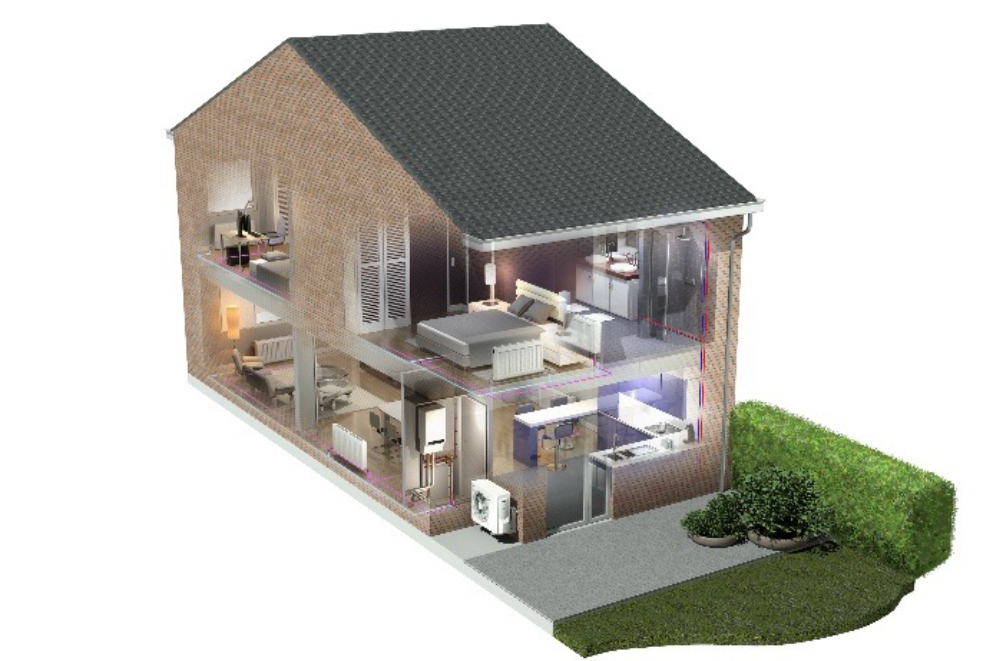

Figure 5 – Illustration of hybrid heat pump installation in home
Hybrid systems are systems where any type of heat pump is installed in conjunction with a traditional fossil fuel boiler; they are particularly useful for harder to heat properties. In a hybrid system, the boiler acts as a turbo to boost the heating during the coldest periods of the year, giving you the best performance of a heat pump and a traditional boiler.
